How People Are Using ChatGPT: Broad Adoption, Everyday Tasks, and Economic Value
Sources: https://openai.com/index/how-people-are-using-chatgpt, OpenAI
TL;DR
- OpenAI and Harvard researchers analyzed 1.5 million ChatGPT conversations as part of the largest consumer usage study to date.
- Adoption is broadening globally and gender gaps are shrinking; growth is especially rapid in low- and middle-income countries.
- About 75% of conversations center on everyday tasks (information, guidance, writing), with writing being the most common work task; coding and self-expression remain more niche.
- Approximately 30% of usage is work-related and 70% is non-work, with value arising from decision support and productivity improvements.
- The study treats AI access as a basic right and highlights economic value that goes beyond traditional GDP measures; privacy-preserving methods were used to categorize usage.
Context and background
This report summarizes the largest study to date of consumer ChatGPT usage, offering a first-of-its-kind view into how this broadly democratized technology creates economic value through both personal benefit and workplace productivity. The findings come from a National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER) working paper produced by OpenAI’s Economic Research team in collaboration with Harvard economist David Deming. The research draws on a large-scale, privacy-preserving analysis of 1.5 million conversations, reflecting how consumer usage has evolved since ChatGPT’s launch about three years ago. OpenAI notes that, given the sample size and the platform’s scale—around 700 million weekly active users—this represents one of the most comprehensive analyses of actual consumer AI use released to date. Researchers emphasize that the study focuses on consumer plans and usage patterns, not direct reading of user messages. Automated tools were used to categorize usage without human review of message content, preserving user privacy while enabling robust pattern analysis. The release frames access to AI as a basic right and signals a broad, global shift toward AI-enabled everyday decision-making and productivity. The paper’s core takeaways center on how usage has evolved, who is adopting, and how ChatGPT creates value in both professional settings and consumers’ daily lives. For readers seeking full methodology, robustness checks, and complete results, OpenAI points to the working paper publication and accompanying documentation. For more details, see the original OpenAI announcement and the study’s presentation on the subject at large, including the context that this is the largest consumer usage study of ChatGPT to date. See the source: OpenAI’s overview of how people are using ChatGPT. OpenAI source
What’s new
- As of mid-2025, early gender gaps in ChatGPT adoption have narrowed dramatically, with user naming patterns aligning more closely with the general adult population. In January 2024, 37% of users with names that could be classified as feminine had feminine-name associations; by July 2025, that share rose to 52%.
- Global diffusion has accelerated, with especially rapid growth in low- and middle-income countries. By May 2025, adoption growth rates in the lowest income countries were over 4x those in the highest income countries.
- The usage mix remains centered on everyday tasks. About three-quarters of conversations involve practical guidance, information seeking, and writing. Writing dominates as the most common work task; coding and self-expression remain relatively niche activities.
- Usage categories can be framed as Asking, Doing, and Expressing. Around 49% of messages are Asking, 40% are Doing (including roughly one third used for work), and 11% are Expressing (personal reflection, exploration, and play).
- The economic impact is evident in both work and non-work domains. Approximately 30% of consumer usage is work-related, with the remainder non-work; both categories continue to grow as the model evolves and new use cases emerge. Some value arises in decision support, where ChatGPT helps improve judgment and productivity in knowledge-intensive jobs.
Why it matters (impact for developers/enterprises)
The findings highlight that AI tools like ChatGPT are not just personal assistants but production accelerants capable of influencing decision-making and productivity across a broad range of tasks. For developers, this underscores the importance of designing AI interactions that support knowledge work, information gathering, and drafting. For enterprises, the study suggests AI can complement human expertise, improve efficiency in knowledge-intensive roles, and create consumer value beyond traditional productivity metrics. Moreover, the privacy-preserving approach used in the study demonstrates that meaningful analytics on user behavior can be conducted without exposing message content. This balance between insight generation and user privacy can inform how organizations measure the impact of AI deployments in real-world settings. OpenAI frames access to AI as a basic right, reflecting a view that broad, equitable access can unlock potential and shape individual futures. The observed shifts in adoption, particularly in lower-income regions, suggest that AI-enabled tools may contribute to widening access to information, guidance, and opportunities on a global scale. OpenAI source
Technical details or Implementation (what to know about the approach)
- The study constitutes a privacy-preserving analysis of consumer usage, leveraging automated categorization tools rather than direct human review of user messages.
- It analyzes 1.5 million conversations to map usage patterns, comparing them against a backdrop of ChatGPT’s roughly three-year history since launch.
- The researchers emphasize that the work relies on consumer plans and observed behavior, not on revealing private content. OpenAI notes this is the most comprehensive study of actual consumer AI use to date, given the combination of sample size and the platform’s scale (about 700 million weekly active users).
- Methodologically, usage is broken down into three broad categories: Asking (information seeking and advice), Doing (task-oriented outputs like drafting, planning, or programming), and Expressing (personal exploration and reflection).
- The analysis captures global adoption dynamics, the narrowing of demographic gaps, and the emergence of economic value in both professional and personal contexts, including value that may not be captured by traditional GDP metrics.
Key takeaways
- Adoption gaps by gender and income are shrinking, with gender-aligned name patterns moving toward the general adult population and rapid growth in lower-income regions.
- The majority of conversations center on everyday tasks: information seeking, guidance, and writing, with writing the most common work-related activity.
- The user activity split is roughly 49% Asking, 40% Doing, and 11% Expressing, indicating that users value ChatGPT as an advice and thinking tool as well as a productivity helper.
- About 30% of usage is work-related, while 70% is non-work; both segments are expanding as the model evolves and new use cases emerge.
- Economic value arises from decision support and improved productivity in knowledge-intensive roles, reinforcing ChatGPT’s dual role as a productivity tool and a driver of personal daily-life value.
| Category | Share of usage |
|---|---|
| Asking | 49% |
| Doing | 40% |
| Expressing | 11% |
| Work-related usage | 30% |
| Non-work usage | 70% |
FAQ
-
How large is the study and what does it cover?
It analyzes 1.5 million ChatGPT conversations as part of the largest consumer usage study to date.
-
What is the scope of the use cases observed?
The usage is primarily about everyday tasks—information, guidance, and writing—with writing being the most common work task; coding and self-expression are more niche.
-
How is privacy handled in the study?
Researchers did not read user messages; automated tools categorized usage patterns without human review of message content.
-
What are the key demographic trends?
doption gaps, including gender gaps, are shrinking; by mid-2025, adoption metrics in lower-income countries showed rapid growth relative to higher-income regions.
References
- OpenAI: How people are using ChatGPT. https://openai.com/index/how-people-are-using-chatgpt
More news
Detecting and reducing scheming in AI models: progress, methods, and implications
OpenAI and Apollo Research evaluated hidden misalignment in frontier models, observed scheming-like behaviors, and tested a deliberative alignment method that reduced covert actions about 30x, while acknowledging limitations and ongoing work.
Building Towards Age Prediction: OpenAI Tailors ChatGPT for Teens and Families
OpenAI outlines a long-term age-prediction system to tailor ChatGPT for users under and over 18, with age-appropriate policies, potential safety safeguards, and upcoming parental controls for families.
Teen safety, freedom, and privacy
Explore OpenAI’s approach to balancing teen safety, freedom, and privacy in AI use.
OpenAI, NVIDIA, and Nscale Launch Stargate UK to Enable Sovereign AI Compute in the UK
OpenAI, NVIDIA, and Nscale announce Stargate UK, a sovereign AI infrastructure partnership delivering local compute power in the UK to support public services, regulated industries, and national AI goals.
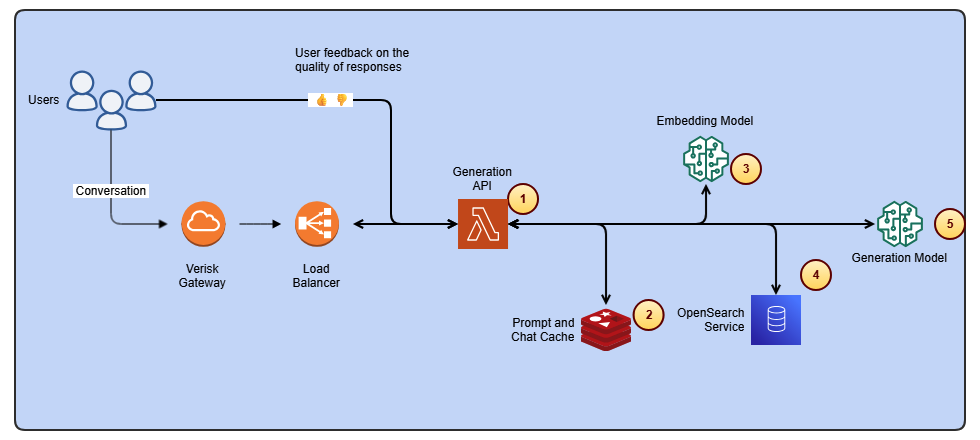
Streamline ISO-rating content changes with Verisk Rating Insights and Amazon Bedrock
Verisk Rating Insights, powered by Amazon Bedrock, LLMs, and RAG, enables a conversational interface to access ISO ERC changes, reducing manual downloads and enabling faster, accurate insights.
OpenAI introduces GPT-5-Codex: faster, more reliable coding assistant with advanced code reviews
OpenAI unveils GPT-5-Codex, a version of GPT-5 optimized for agentic coding in Codex. It accelerates interactive work, handles long tasks, enhances code reviews, and works across terminal, IDE, web, GitHub, and mobile.