OpenAI partners with US CAISI and UK AISI to strengthen AI safety and security
Sources: https://openai.com/index/us-caisi-uk-aisi-ai-update, OpenAI
TL;DR
- OpenAI continues and expands its voluntary partnerships with the US Center for AI Standards and Innovation (CAISI) and the UK AI Security Institute (UK AISI) to strengthen safe deployment of frontier AI. OpenAI CAISI update
- The collaborations include joint red-teaming of safeguards against biological misuse, end-to-end testing of products for security issues, and rapid feedback loops to resolve vulnerabilities. OpenAI CAISI update
- CAISI identified two novel security vulnerabilities in OpenAI’s ChatGPT Agent with a proof-of-concept attack that could bypass protections with about 50% success; OpenAI fixed the issues within one business day. OpenAI CAISI update
- Since May, UK AISI has been red-teaming safeguards against biological misuse across OpenAI’s Agent and GPT‑5, with a weekly cadence and access to non-public tools to accelerate improvements. OpenAI CAISI update
- The collaboration demonstrates how government and industry can work together to raise safety standards, improve product security, and foster responsible adoption of AI.
Context and background
OpenAI notes that developing and deploying AI that is secure and useful is core to its mission of ensuring that AGI benefits all of humanity, and that this requires ongoing work with national authorities and standards bodies. OpenAI entered into voluntary agreements with CAISI (the US Center for AI Standards and Innovation) and the UK AI Security Institute (UK AISI) as part of its approach to secure frontier AI deployment. These partnerships reflect the belief that frontier AI development should occur in close collaboration with allied governments that bring expertise in machine learning, national security, and metrology. For more than a year, OpenAI has partnered with CAISI to evaluate OpenAI models’ capabilities in cyber, chemical-biological, and other national security-relevant domains. This collaboration has expanded to include emerging product security challenges and red-teaming of OpenAI’s agentic AI systems, including the ChatGPT Agent product. OpenAI CAISI update The work with CAISI builds on OpenAI’s broader security program and internal testing, and the collaboration with UK AISI complements earlier efforts on safeguarding against biological misuse. UK AISI’s involvement began in May with red-teaming of safeguards across OpenAI’s systems, including the safeguards in both ChatGPT Agent and GPT‑5, as part of an ongoing program rather than tied to a single launch. The collaboration emphasizes rapid feedback loops and close coordination between OpenAI’s technical teams and external evaluators. OpenAI CAISI update
What’s new
The update highlights several new aspects of the CAISI/UK AISI collaborations:
- Agentic AI security focus: OpenAI and CAISI conducted red-teaming of OpenAI’s agentic AI systems, including external evaluators working with OpenAI to identify and fix security vulnerabilities in real time. This included a preliminary step into testing approaches for agentic systems. OpenAI CAISI update
- July collaboration results: CAISI gained early access to ChatGPT Agent, helping to understand system architecture and later performing red-teaming of the released system. The outcome included discovery of novel vulnerabilities and remediation. OpenAI CAISI update
- Vulnerabilities and remediation: CAISI identified two novel security vulnerabilities that, under certain conditions, could let a sophisticated attacker bypass safeguards and remotely control the agent’s session and impersonate a user on other websites. A proof-of-concept attack demonstrated a ~50% success rate. After reporting, OpenAI fixed these issues within one business day. The work underscores the need to chain traditional cyber vulnerabilities with AI vulnerabilities to test guardrails. OpenAI CAISI update
- Biological safeguards testing with UK AISI: As part of ongoing collaboration, UK AISI began red-teaming OpenAI’s safeguards against biological misuse (as defined by OpenAI policies) in May, covering safeguards in both ChatGPT Agent and GPT‑5. The collaboration uses iterative testing, with frequent meetings (roughly weekly) and bespoke configurations to test weaknesses.
- Access and testing environment: UK AISI received in-depth access to systems and non-public testing resources to enable deeper testing, which helped surface failures that would be harder for external attackers to reproduce. The teams operated in iterative cycles of probing, strengthening safeguards, and retesting. OpenAI CAISI update Together, these efforts have led to improvements across monitoring, product configuration, and policy enforcement, and have produced concrete vulnerability reports and fixes that benefited end users and the security of widely deployed OpenAI products. UK AISI’s involvement also contributed to strengthening the full moderation stack and related safeguards. OpenAI CAISI update
Why it matters (impact for developers/enterprises)
The collaboration with CAISI and UK AISI signals a multi-layered approach to AI security that combines external evaluation with internal hardening. By validating agentic capabilities, stress-testing safeguards against misuse, and rapidly addressing discovered vulnerabilities, OpenAI seeks to raise industry standards and bolster trust in AI deployments. As OpenAI notes, close technical partnerships with organizations equipped to rigorously evaluate AI systems help strengthen confidence in the security of these systems for end users and enterprises alike. OpenAI CAISI update For developers and enterprises, the implications include more robust safeguards across products that rely on agentic AI, improved monitoring and moderation, and faster turnaround on fixes when vulnerabilities are discovered. The ongoing collaboration demonstrates how governments, standards bodies, and industry can work together to evaluate, improve, and responsibly deploy frontier AI. OpenAI CAISI update
Technical details or Implementation
The joint program blends traditional cybersecurity testing with AI-specific red-teaming, yielding concrete improvements in safeguards and product security. Key elements include:
- Dual-domain red-teaming: CAISI’s expertise in cybersecurity and AI agent security was applied to test OpenAI’s agentic systems, including the ChatGPT Agent, for vulnerabilities that could affect system integrity and user safety. OpenAI CAISI update
- End-to-end testing: OpenAI and partners conducted end-to-end testing of product configurations and responses, addressing vulnerabilities that could arise anywhere from model outputs to the user experience. OpenAI CAISI update
- Rapid vulnerability triage: UK AISI contributed to a rapid feedback loop, surfacing more than a dozen vulnerability reports, with some leading to engineering fixes and policy or classifier improvements. OpenAI CAISI update
- Monitoring and safeguards hardening: Improvements to the monitoring stack were measured against universal jailbreaks identified by UK AISI, strengthening detection and mitigation capabilities. OpenAI CAISI update
- Custom testing configurations: OpenAI created testing configurations tailored to results from UK AISI to enable more effective evaluation of safeguards. OpenAI CAISI update
- Non-public testing resources: The collaboration allowed access to non-public tools and design details, enabling more thorough red-teaming than would be possible with public materials alone. OpenAI CAISI update
- Broader safeguards improvements: The agentic safeguards build on prior work to prevent biological misuse, illustrating how multiple layers of safety interact across the product. The ongoing program includes testing across model responses and the end-to-end product experience. OpenAI CAISI update
Key takeaways
- External evaluation accelerates internal security improvements for AI systems.
- Red-teaming for agentic AI and biological-misuse safeguards can reveal novel attack paths that mix traditional software vulnerabilities with AI-specific weaknesses.
- Rapid triage and fixes—often within a business day—are achievable through close collaboration and access to non-public testing resources.
- Ongoing, iterative testing and weekly coordination help sustain stronger safeguards across deployment scenarios.
- Partnerships with standards bodies and security institutes can raise industry-wide confidence in AI safety.
FAQ
-
What is CAISI?
The US Center for AI Standards and Innovation, a US research and standards body OpenAI has voluntary agreements with.
-
What is UK AISI?
The UK AI Security Institute, with which OpenAI engaged in ongoing red-teaming of safeguards against biological misuse and other risk areas.
-
What vulnerabilities were found and how were they handled?
CAISI identified two novel security vulnerabilities in ChatGPT Agent that could, under certain conditions, allow bypassing protections and remote control of a session; a proof-of-concept attack achieved ~50% success. OpenAI fixed the issues within one business day after disclosure. [OpenAI CAISI update](https://openai.com/index/us-caisi-uk-aisi-ai-update)
-
Why does this matter for developers and enterprises?
The collaboration strengthens safeguards and product security, improves monitoring and testing, and demonstrates constructive government-industry collaboration aimed at safer deployment of frontier AI.
References
More news
First look at the Google Home app powered by Gemini
The Verge reports Google is updating the Google Home app to bring Gemini features, including an Ask Home search bar, a redesigned UI, and Gemini-driven controls for the home.
Shadow Leak shows how ChatGPT agents can exfiltrate Gmail data via prompt injection
Security researchers demonstrated a prompt-injection attack called Shadow Leak that leveraged ChatGPT’s Deep Research to covertly extract data from a Gmail inbox. OpenAI patched the flaw; the case highlights risks of agentic AI.
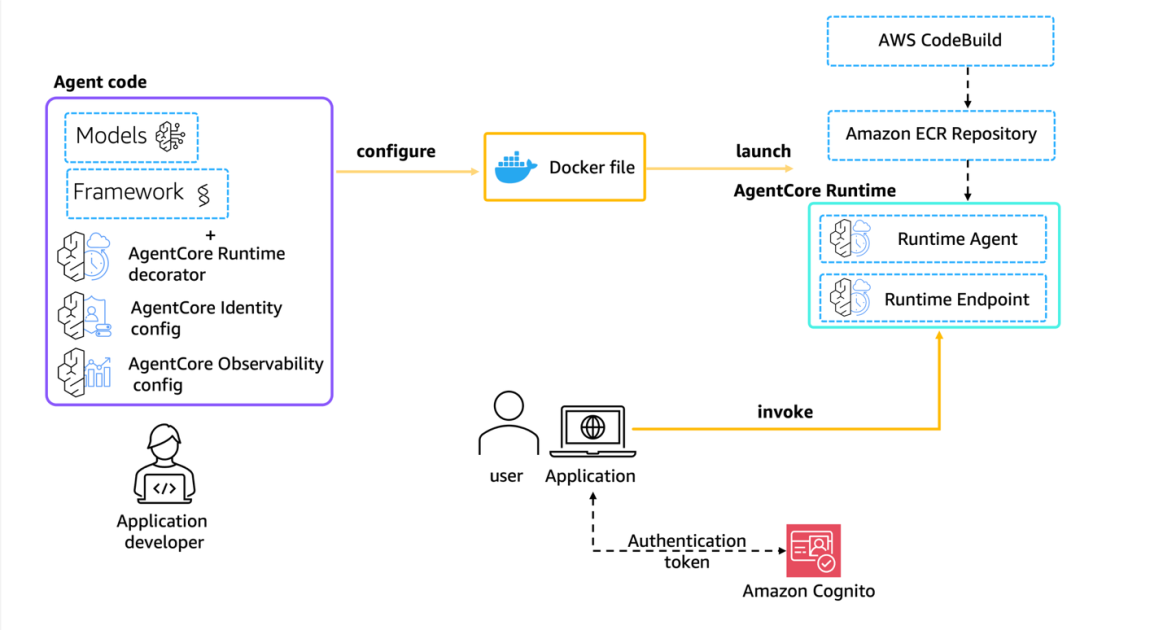
Move AI agents from proof of concept to production with Amazon Bedrock AgentCore
A detailed look at how Amazon Bedrock AgentCore helps transition agent-based AI applications from experimental proof of concept to enterprise-grade production systems, preserving security, memory, observability, and scalable tool management.
Predict Extreme Weather in Minutes Without a Supercomputer: Huge Ensembles (HENS)
NVIDIA and Berkeley Lab unveil Huge Ensembles (HENS), an open-source AI tool that forecasts low-likelihood, high-impact weather events using 27,000 years of data, with ready-to-run options.
Scaleway Joins Hugging Face Inference Providers for Serverless, Low-Latency Inference
Scaleway is now a supported Inference Provider on the Hugging Face Hub, enabling serverless inference directly on model pages with JS and Python SDKs. Access popular open-weight models and enjoy scalable, low-latency AI workflows.
Google expands Gemini in Chrome with cross-platform rollout and no membership fee
Gemini AI in Chrome gains access to tabs, history, and Google properties, rolling out to Mac and Windows in the US without a fee, and enabling task automation and Workspace integrations.