NVIDIA Hardware Innovations and Open Source Contributions Shape AI
Sources: https://developer.nvidia.com/blog/nvidia-hardware-innovations-and-open-source-contributions-are-shaping-ai, https://developer.nvidia.com/blog/nvidia-hardware-innovations-and-open-source-contributions-are-shaping-ai/, NVIDIA Dev Blog
TL;DR
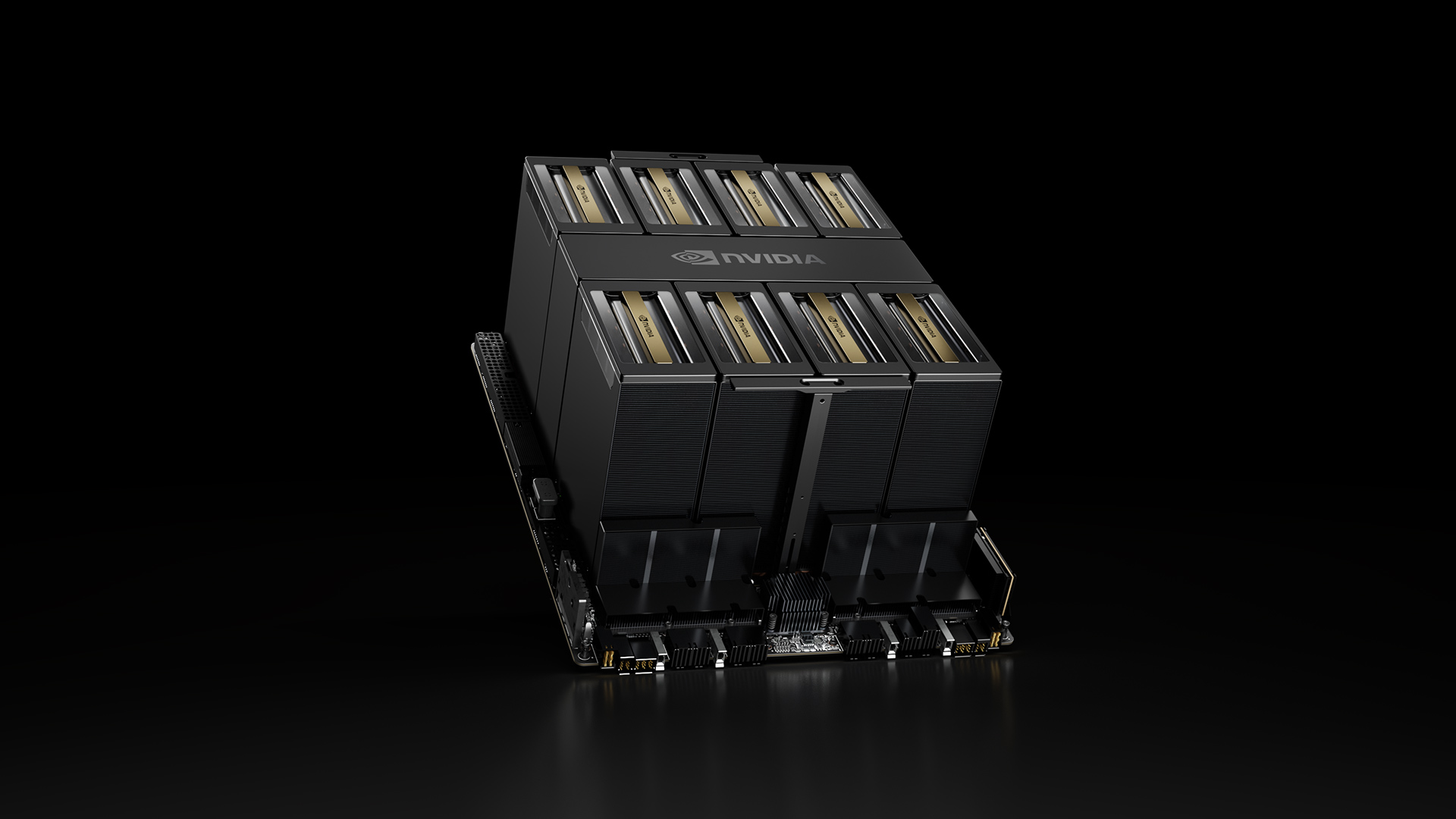
- NVIDIA’s Blackwell AI superchip combines fifth-generation Tensor Cores with a 4-bit floating-point format (NVFP4) and NVLink-72 to deliver massive compute with high accuracy for demanding AI workloads.
- The company couples this hardware with a robust open-source stack: 1,000+ tools on NVIDIA GitHub, and 450+ models with 80+ datasets on Hugging Face, spanning data prep to deployment.
- Open models, datasets, and frameworks enable scaling AI from prototype to production within a fully open ecosystem, with end-to-end pipelines spanning RAPIDS, NeMo, and Dynamo.
- Real-world performance gains include up to 4x faster interactivity on GPT-OSS 120B (OpenAI GPT-OSS 120B) on NVIDIA B200 Blackwell GPUs and up to 2.5x higher throughput on DeepSeek-R1 671B with GB200 NVL72; Nemotron achieves up to 6x throughput over competing open models. NVIDIA Blog
- The open ecosystem is reinforced by tools like TensorRT-LLM, CUTLASS, and Dynamo, enabling scalable, optimized inference across PyTorch, TensorRT-LLM, vLLM, and SGLang. NVIDIA Blog
Context and background
Open source AI models such as Cosmos, DeepSeek, Gemma, GPT-OSS, Llama, Nemotron, Phi, Qwen, and many others are described as foundational to AI innovation. These models democratize AI by making weights, architectures, and training methodologies freely available to researchers, startups, and organizations worldwide. Developers can learn and build on techniques like mixture-of-experts (MoE), novel attention kernels, and post-training for reasoning—without starting from scratch. NVIDIA frames this democratization as amplified by broad access to its hardware and open source software designed to accelerate AI from the cloud and data center to edge devices. NVIDIA Blog NVIDIA’s Blackwell GPU architecture is described as a purpose-built AI superchip that packs fifth-generation Tensor Cores and NVFP4 (4-bit floating-point) to deliver massive compute with high accuracy. It integrates NVLink‑72 for ultra-fast GPU-to-GPU communication and scaling across multi-GPU configurations for demanding AI workloads. Blackwell GPUs also include second-generation Transformer Engines and NVLink Fusion to bolster performance and efficiency. NVIDIA Blog A key theme is the optimization of the entire software stack to deliver peak AI performance: open source tools, models, and datasets are released to accelerate development at the system level. NVIDIA points to more than 1,000 open source tools available through NVIDIA GitHub repositories and NVIDIA’s Hugging Face collections offering 450+ models and 80+ datasets. The open source software stack spans from foundational data processing to complete AI development and deployment frameworks, with CUDA-X libraries accelerating entire ecosystems of tools. NVIDIA Blog In support of end-to-end AI workflows, RAPIDS accelerates data preparation and ETL pipelines, enabling AI workloads to run end-to-end on GPUs and avoiding CPU bottlenecks. The NeMo framework provides end-to-end training for large language models (LLMs), multimodal models, and speech models, scalable from a single GPU to thousands of nodes. PhysicsNeMo introduces physics-informed ML to integrate physical laws into neural networks, aiding digital twin development and scientific simulations. BioNeMo targets life sciences with pretrained models, protein structure prediction, and drug discovery capabilities, delivering tools as accelerated NIM microservices. These frameworks leverage NCCL for multi-GPU and multi-node communication. NVIDIA Blog Together with the NeMo family, TensorRT provides an inference stack (including TensorRT-LLM and TensorRT Model Optimizer) that optimizes kernels and quantization for deploying models at scale. TensorRT-LLM leverages Blackwell instructions and FP4 to push performance and memory efficiency further. For developers building custom kernels, CUTLASS provides CUDA C++ templates to streamline high-performance GEMM operations. NVIDIA Dynamo is an open-source, framework-agnostic inference-serving platform designed to scale reasoning AI by disaggregating inference stages and enabling LLM-aware scheduling; it also includes NIXL, a high-throughput, low-latency data-movement library for AI inference environments. Dynamo 0.4 with TensorRT-LLM shows impressive results: up to 4x faster interactivity for GPT-OSS 120B on B200 Blackwell GPUs without throughput tradeoffs, and 2.5x higher throughput per GPU on DeepSeek-R1 671B with GB200 NVL72. NVIDIA Blog
What’s new
NVIDIA emphasizes a comprehensive open-source approach that combines cutting-edge hardware with a broad software stack. The Blackwell GPU family introduces 4-bit floating-point precision (NVFP4) and next-generation interconnects (NVLink-72) along with second-generation Transformer Engines and NVLink Fusion to enable scalable, efficient AI workloads. The software ecosystem adds extensive open models and datasets on Hugging Face, with hundreds of models and thousands of datasets distributed under permissive licenses like the NVIDIA Open Model License, all designed to run on Blackwell hardware. In addition, products such as Cosmos provide generative models and tools for world generation and understanding, with tokenizers and data pipelines released under open licenses to accelerate physical AI development. NVIDIA Blog The pipeline now starts with RAPIDS for data preparation and analytics, enabling end-to-end GPU acceleration going into model training with NeMo, PhysicsNeMo, BioNeMo, and related tools. Models can be trained and tuned at scale for Hugging Face/PyTorch and Megatron ecosystems, followed by optimized deployment via the TensorRT stack and Dynamo serving. Open models and datasets are available on platforms like Hugging Face, with open licenses ensuring broad adoption and collaboration. The Cosmos family, built for physical AI tasks, complements Omniverse SDKs and OpenUSD-based data aggregation for sim-to-real simulations in robotics and industrial use cases. NVIDIA Blog NVIDIA also highlights its open-source contributions to foundational projects and foundations, including the Linux Kernel, Python, PyTorch, Kubernetes, JAX, and ROS, and involvement with organizations such as the Linux Foundation, PyTorch Foundation, Python Software Foundation, Cloud Native Computing Foundation, Open Source Robotics Foundation, and The Alliance for OpenUSD. NVIDIA Blog
Why it matters (impact for developers/enterprises)
- For developers, the ecosystem provides an open, rapidly evolving software stack with thousands of tools and hundreds of pre-trained models to experiment with and customize. This reduces time to prototype and test AI ideas on cutting-edge hardware like Blackwell. NVIDIA Blog
- For enterprises, the ability to scale inference and reasoning with high-throughput systems like Dynamo and TensorRT-LLM, combined with efficient multi-GPU and multi-node communication (NCCL), enables production-ready AI deployments at scale. Real-world results cited include faster interactivity and higher per-GPU throughput on large models, with cost-aware inference. NVIDIA Blog
- For researchers and scientists, PhysicsNeMo and BioNeMo bring physics-informed ML and biology-centric AI capabilities, accelerating digital twins, simulations, protein design, and drug discovery, while staying within an open, extensible framework. NVIDIA Blog
Technical details or Implementation
- Hardware foundations: Blackwell architecture with fifth-generation Tensor Cores, NVFP4 (4-bit FP), NVLink‑72, second-generation Transformer Engines, and NVLink Fusion. These features drive high-precision AI inference and training at scale. NVIDIA Blog
- Open-source ecosystem: over 1,000 tools on NVIDIA GitHub and 450+ models with 80+ datasets on Hugging Face. The ecosystem spans data processing (RAPIDS) to model training (NeMo, PhysicsNeMo, BioNeMo) and multi-framework support (PyTorch, Megatron, Hugging Face). NVIDIA Blog
- Inference and deployment: TensorRT-LLM with FP4-optimized kernels, TensorRT Model Optimizer, and CUTLASS for high-performance GEMM kernels. Dynamo serves inference at scale with NIXL for high-throughput data movement. Real-world Dynamo results show substantial throughput and latency improvements for large models. NVIDIA Blog
- Open models and sim-to-real: Cosmos (Predict, Transfer, Reason) with tokenizers and data pipelines; Omniverse SDKs/OpenUSD enable real-time rendering and physics schemas for industrial and robotics simulations; Cosmos-based sim-to-real pipelines help train AI that functions in real-world environments. NVIDIA Blog
- End-to-end data pipelines: RAPIDS accelerates raw data processing and ETL; NeMo enables scalable training; CUDA-X libraries tie together the software stack to accelerate the entire AI lifecycle on Blackwell. NVIDIA Blog
Key takeaways
- The AI ecosystem around NVIDIA is orchestration of hardware innovations (Blackwell) and a broad open-source stack (RAPIDS, NeMo, Cosmos, Dynamo, TensorRT, CUTLASS, etc.).
- Open models and datasets combined with permissive licenses accelerate collaboration and deployment at scale.
- End-to-end pipelines—from data prep to training to serving—are designed to run entirely within an open ecosystem on Blackwell hardware.
- Concrete performance gains demonstrate the value of this approach: faster interactivity and higher throughput on large models using Dynamo and TensorRT-LLM, plus improved per-GPU efficiency on newer NVL and NVFP4 capabilities. NVIDIA Blog
FAQ
-
What makes Blackwell unique for AI workloads?
It combines fifth-generation Tensor Cores, NVFP4 4-bit FP, NVLink‑72 for fast GPU interconnect, and second-generation Transformer Engines to deliver high compute and efficiency for modern AI tasks. [NVIDIA Blog](https://developer.nvidia.com/blog/nvidia-hardware-innovations-and-open-source-contributions-are-shaping-ai/)
-
How does Dynamo fit into the AI stack?
Dynamo is a framework-agnostic inference-serving platform designed to scale reasoning AI by disaggregating inference stages and using intelligent LLM-aware scheduling; it supports PyTorch, TensorRT-LLM, vLLM, and SGLang. [NVIDIA Blog](https://developer.nvidia.com/blog/nvidia-hardware-innovations-and-open-source-contributions-are-shaping-ai/)
-
Where can developers access open-source tools and models?
Through NVIDIA’s GitHub repositories and Hugging Face collections, which host thousands of tools, models, and datasets under permissive licenses. [NVIDIA Blog](https://developer.nvidia.com/blog/nvidia-hardware-innovations-and-open-source-contributions-are-shaping-ai/)
-
What is Cosmos and why is it important?
Cosmos is a suite of generative models and tools for world generation and understanding, with a focus on sim-to-real AI development for physical AI applications. [NVIDIA Blog](https://developer.nvidia.com/blog/nvidia-hardware-innovations-and-open-source-contributions-are-shaping-ai/)
References
- NVIDIA Dev Blog: NVIDIA Hardware Innovations and Open Source Contributions Are Shaping AI. https://developer.nvidia.com/blog/nvidia-hardware-innovations-and-open-source-contributions-are-shaping-ai/
More news
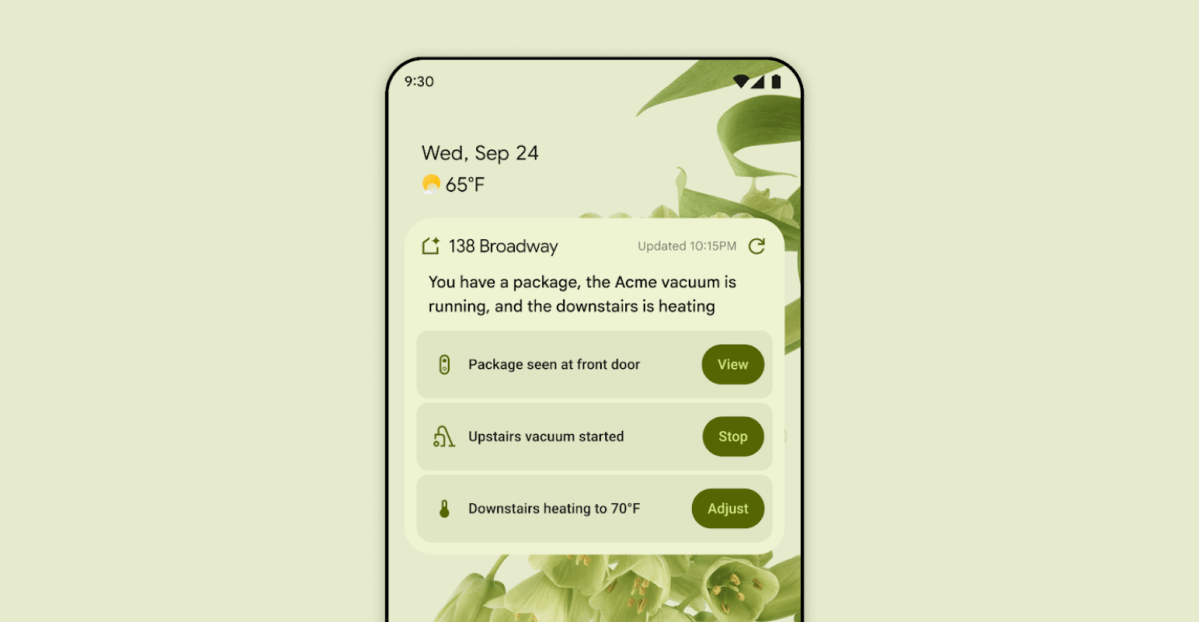
First look at the Google Home app powered by Gemini
The Verge reports Google is updating the Google Home app to bring Gemini features, including an Ask Home search bar, a redesigned UI, and Gemini-driven controls for the home.
NVIDIA HGX B200 Reduces Embodied Carbon Emissions Intensity
NVIDIA HGX B200 lowers embodied carbon intensity by 24% vs. HGX H100, while delivering higher AI performance and energy efficiency. This article reviews the PCF-backed improvements, new hardware features, and implications for developers and enterprises.
Shadow Leak shows how ChatGPT agents can exfiltrate Gmail data via prompt injection
Security researchers demonstrated a prompt-injection attack called Shadow Leak that leveraged ChatGPT’s Deep Research to covertly extract data from a Gmail inbox. OpenAI patched the flaw; the case highlights risks of agentic AI.
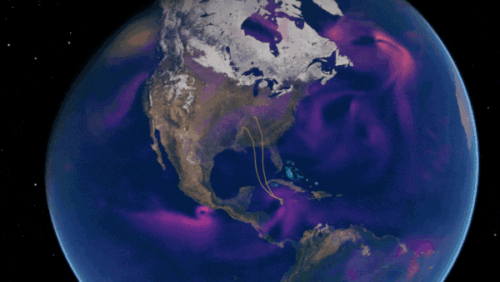
Predict Extreme Weather in Minutes Without a Supercomputer: Huge Ensembles (HENS)
NVIDIA and Berkeley Lab unveil Huge Ensembles (HENS), an open-source AI tool that forecasts low-likelihood, high-impact weather events using 27,000 years of data, with ready-to-run options.
Scaleway Joins Hugging Face Inference Providers for Serverless, Low-Latency Inference
Scaleway is now a supported Inference Provider on the Hugging Face Hub, enabling serverless inference directly on model pages with JS and Python SDKs. Access popular open-weight models and enjoy scalable, low-latency AI workflows.
Google expands Gemini in Chrome with cross-platform rollout and no membership fee
Gemini AI in Chrome gains access to tabs, history, and Google properties, rolling out to Mac and Windows in the US without a fee, and enabling task automation and Workspace integrations.