Q&A: DoorDash CPO Mariana Garavaglia on Scaling AI, Literacy, and Employee Impact
Sources: https://openai.com/index/doordash-mariana-garavaglia, openai.com
TL;DR
- DoorDash treats AI adoption as an operator-led transformation, scaling literacy and access across the organization.
- The approach rests on three layers: access and literacy, internal data integration, and AI agents for trusted tasks.
- AI is used to augment human judgment, synthesize feedback, and automate routine workflows, not just to automate.
- OpenAI tools, including ChatGPT Enterprise and APIs, power both internal workflows and external platforms, with millions of daily interactions.
Context and background
DoorDash positions itself as one of the world’s leading local commerce platforms, with an operator culture where everyone is expected to understand the consumer experience and think with the speed and mindset of a product team. Long before AI advances, the company ran continuous experiments—from conversion rates to marketing efficacy. AI now accelerates the pace of learning, testing, and iteration, enabling faster cycles of insight and action. IT and HR collaborate closely, as tooling becomes a core responsibility for both teams. The overarching goal is to augment core workflows and improve the way employees experience their work. The organization emphasizes democratizing automation and workflow creation. Non-technical employees can, for example, build scripts to automate document uploads—reducing manual work and lowering the barrier to delivering tailored solutions for use cases. This shift is part of a broader effort to empower more people to become technical creators within the enterprise.
What’s new
DoorDash has begun measuring AI literacy and impact through two foundational metrics: adoption and frequency of use. Engineers can now build in minutes what used to take days, and adoption has been fast and organic. The company is also examining how licenses are distributed across teams and how frequently tools are used. In addition, AI literacy is being integrated into performance frameworks, focusing on competencies like willingness to adopt new tools and a learning mindset. Two notable examples illustrate the broader impact: performance reviews and employee surveys. AI helps surface key themes, strengths, and growth opportunities from feedback, turning raw data into clearer takeaways. For surveys, AI identifies patterns and generates actionable summaries for managers, and even supports workflows that produce Mad Libs–style action plans showing how team responses evolve. While executive coaching is not yet AI-driven, DoorDash is building predictive models to assess executive performance using cohort data, interview assessments, and reference checks, with coaching filling in any gaps as needed. The HR and IT teams benefit from dedicated engineers and engineering resources focused on internal workflows, enabling a unified strategy and faster iteration. The goal is to deploy “agentic capabilities” through tools and talent, delivering personalized experiences and support at scale. DoorDash uses ChatGPT Enterprise across the organization—technical and non-technical teams alike—and OpenAI APIs power the customer service platform (3 million chats per month) as well as internal review moderation and support workflows.
Why it matters (impact for developers/enterprises)
The approach democratizes AI, allowing non-engineers to create tailored automations and workflows, thereby accelerating internal value delivery and personal development. By integrating AI literacy into the performance framework, the company emphasizes a learning mindset and broader adoption. The emphasis on augmenting human judgment alongside automation is designed to preserve critical thinking, while AI handles synthesis, pattern recognition, and routine tasks at scale. The presence of internal engineers within HR and IT fosters a unified strategy, ensuring governance, security, and rapid iteration. For developers and enterprises, the DoorDash model highlights how AI can be embedded into core people processes—performance management, surveys, and development—while maintaining human interpretation as essential. The use of enterprise-grade tools like ChatGPT Enterprise and OpenAI APIs demonstrates how AI can support large-scale customer interactions and internal workflows without sacrificing quality or governance.
Technical details or Implementation
The implementation rests on three layers. First, access and literacy establish how every employee—across roles—can use frontier tools through enterprise rollouts, hackathons, and tutorials. Second, internal data integration removes silos to enable AI-powered search and smarter content delivery. Third, exploration of AI agents focuses on tasks that can be tackled in a smart, trusted way, with the aim of enhancing core workflows rather than pursuing automation for its own sake. This structure supports a broad, scalable AI program that adapts to changing tooling and needs. Operationally, DoorDash emphasizes a strong internal tooling capability. The HR and IT teams include dedicated engineers and engineering resources to move up the stack and realize agentic capabilities. This joint capability helps translate strategy into practical solutions and reduces time-to-value for new AI-enhanced workflows. Two concrete platforms drive the program: ChatGPT Enterprise across the organization (including finance, sales, operations, IT, and marketing) and OpenAI APIs powering customer service (3 million chats per month) as well as internal review moderation and support workflows. This combination enables a consistent, governed AI experience across both external interactions and internal processes.
A structured view of the AI enablement layers
| Layer | Focus |
| Example outcomes |
|---|
| --- |
| --- |
| Access and literacy |
| Non-technical roles use copilots via enterprise rollouts and tutorials |
| Internal data integration |
| Smarter, data-driven content and faster insights |
| AI agents |
| Improved efficiency, personalized supports, and scalable automation |
Key takeaways
- AI adoption at DoorDash is an operator-led, three-layer program focused on access, data, and agent-enabled workflows.
- AI is used to augment human judgment, not replace it, with a clear emphasis on governance and human interpretation.
- Non-engineers can participate in automation and content creation, broadening opportunity across the workforce.
- Tools like ChatGPT Enterprise and OpenAI APIs are integrated across the organization to support both customer-facing and internal processes.
- The company links AI literacy to performance frameworks to encourage a growth mindset and durable adoption.
FAQ
-
What metrics does DoorDash use to measure AI literacy and adoption?
The company uses foundational metrics such as adoption and frequency of use, and is considering distribution of licenses and how tools are used across functions.
-
How does DoorDash ensure AI augments rather than replaces human judgment?
AI is used to surface themes, synthesize feedback, identify patterns, and generate actionable summaries while human interpretation remains essential.
-
Can non-engineers build AI-enabled solutions at DoorDash?
Yes. The organization notes that non-technical employees can create tailored automation and workflows, lowering barriers to innovation.
-
What platforms and APIs drive the AI program?
DoorDash uses ChatGPT Enterprise across the organization and OpenAI APIs to power its customer service platform (3 million chats per month) and internal workflows for review moderation and support.
References
More news
First look at the Google Home app powered by Gemini
The Verge reports Google is updating the Google Home app to bring Gemini features, including an Ask Home search bar, a redesigned UI, and Gemini-driven controls for the home.
Shadow Leak shows how ChatGPT agents can exfiltrate Gmail data via prompt injection
Security researchers demonstrated a prompt-injection attack called Shadow Leak that leveraged ChatGPT’s Deep Research to covertly extract data from a Gmail inbox. OpenAI patched the flaw; the case highlights risks of agentic AI.
Predict Extreme Weather in Minutes Without a Supercomputer: Huge Ensembles (HENS)
NVIDIA and Berkeley Lab unveil Huge Ensembles (HENS), an open-source AI tool that forecasts low-likelihood, high-impact weather events using 27,000 years of data, with ready-to-run options.
Scaleway Joins Hugging Face Inference Providers for Serverless, Low-Latency Inference
Scaleway is now a supported Inference Provider on the Hugging Face Hub, enabling serverless inference directly on model pages with JS and Python SDKs. Access popular open-weight models and enjoy scalable, low-latency AI workflows.
Google expands Gemini in Chrome with cross-platform rollout and no membership fee
Gemini AI in Chrome gains access to tabs, history, and Google properties, rolling out to Mac and Windows in the US without a fee, and enabling task automation and Workspace integrations.
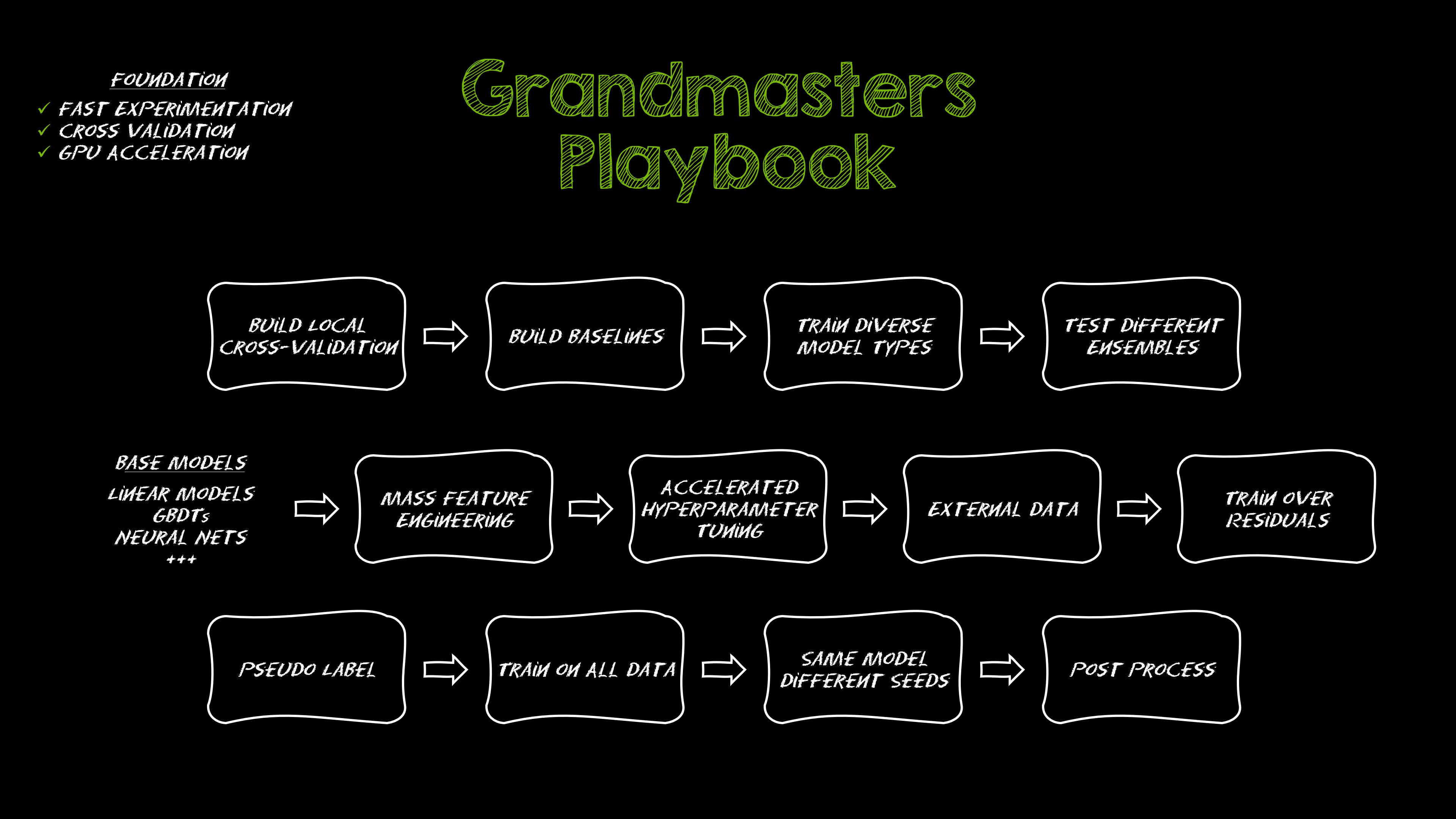
Kaggle Grandmasters Playbook: 7 Battle-Tested Techniques for Tabular Data Modeling
A detailed look at seven battle-tested techniques used by Kaggle Grandmasters to solve large tabular datasets fast with GPU acceleration, from diversified baselines to advanced ensembling and pseudo-labeling.