Dion: The Distributed Orthonormal Update Revolution Is Here
Sources: https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/blog/dion-the-distributed-orthonormal-update-revolution-is-here, microsoft.com
TL;DR
- Dion is a new AI model optimization method designed to boost scalability and performance.
- It achieves gains by orthonormalizing only a top-rank subset of singular vectors.
- The approach enables more efficient training of large models such as LLaMA-3 with reduced overhead.
- A Dion optimizer is available for download.
- The method is distributed, aligning with modern multi-node training workflows about large-scale models.
Context and background
Across AI model development, optimization techniques play a pivotal role in determining training efficiency and resource use. The Dion work, as announced by Microsoft Research, centers on a distributed orthonormal update approach. By focusing on orthonormalizing a top-rank subset of singular vectors, Dion aims to improve scalability and performance relative to existing leading methods, without requiring a full, all-encompassing update of the model parameters. This approach is positioned as a practical path toward more efficient training of very large models, including those in the LLaMA family such as LLaMA-3, by reducing overhead in the update process. The blog post invites readers to download the Dion optimizer to explore its capabilities firsthand. Dion optimizer. In the current landscape of distributed AI training, researchers seek techniques that preserve model fidelity while lowering computation and communication costs. Dion contributes to this goal by prioritizing a subset of singular vectors for orthonormalization, which can streamline updates and potentially shorten training cycles when scaling to larger architectures. While the technical specifics are described in the source post, the high-level premise is clear: a targeted, distributed update strategy may unlock efficiency gains in large-scale training pipelines. For practitioners, the existence of a downloadable optimizer provides a concrete avenue to compare against existing methods and assess its impact within their own training stacks. Dion optimizer.
What’s new
Dion introduces a new optimization method that emphasizes a top-rank subset of singular vectors and applies orthonormal updates in a distributed fashion. The key claims include improved scalability and performance over leading methods, along with reduced overhead when training large models. The approach is designed to be practical for modern AI workloads and is accompanied by a downloadable Dion optimizer for experimentation. In short, Dion proposes a distributed orthonormal update as a new lever for training efficiency on big models such as LLaMA-3. Dion optimizer.
Why it matters (impact for developers/enterprises)
For developers and ML engineers, the prospect of faster, more scalable training pipelines on multi-node clusters is compelling. By orthonormalizing only a top rank of singular vectors, Dion targets the most impactful components of the update process, potentially reducing computational and communication overhead. Enterprises pursuing large-model initiatives can benefit from an approach that aims to lower training costs and improve throughput for models at scale, like LLaMA-3. The availability of a downloadable optimizer invites hands-on evaluation and benchmarking within existing model development and deployment workflows. The blog emphasizes the practical applicability of this method to real-world large-model training scenarios. Dion optimizer.
Technical details or Implementation (high level)
- Core idea: focus on orthonormalizing a top-rank subset of singular vectors and apply the update in a distributed setting. This targeted orthonormalization is intended to deliver scalability and performance benefits without the overhead of full-spectrum updates.
- Distributed execution: the update process is designed to operate across multiple nodes, aligning with contemporary multi-node training workflows.
- Large-model applicability: the approach is presented as suitable for very large models, with examples such as LLaMA-3 mentioned as beneficiaries.
- Availability: the Dion optimizer is provided for download, inviting researchers and practitioners to experiment with the method within their existing pipelines. Dion optimizer.
| Aspect | Dion |
|---|---|
| Core technique | Orthonormalizing a top-rank subset of singular vectors |
| Scale target | Large models (e.g., LLaMA-3) |
| Benefit | Boosted scalability and performance with reduced overhead |
| Availability | Download the Dion optimizer |
Key takeaways
- Dion introduces a distributed approach to orthonormal updates by concentrating on a top-rank subset of singular vectors.
- The method is positioned to improve scalability and performance relative to leading methods, with reduced overhead for large-model training.
- A downloadable Dion optimizer enables hands-on evaluation within existing AI training pipelines.
- The technique is framed for multi-node, distributed training contexts, aligning with current enterprise-scale workflows.
FAQ
-
What is Dion?
Dion is a new AI model optimization method that boosts scalability and performance by orthonormalizing only a top rank subset of singular vectors. [Dion optimizer](https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/blog/dion-the-distributed-orthonormal-update-revolution-is-here).
-
How does it improve training efficiency?
By focusing on orthonormalizing a top-rank subset of singular vectors, Dion aims to deliver improved scalability and performance with reduced overhead in large-model training. [Dion optimizer](https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/blog/dion-the-distributed-orthonormal-update-revolution-is-here).
-
Which models might benefit?
The approach is described as enabling more efficient training of large models such as LLaMA-3. [Dion optimizer](https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/blog/dion-the-distributed-orthonormal-update-revolution-is-here).
-
Where can I get Dion?
The post references a downloadable Dion optimizer labeled for users to download. [Dion optimizer](https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/blog/dion-the-distributed-orthonormal-update-revolution-is-here).
-
Is the update approach distributed?
Yes; the method described is a distributed orthonormal update intended for multi-node training workflows. [Dion optimizer](https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/blog/dion-the-distributed-orthonormal-update-revolution-is-here).
References
More news
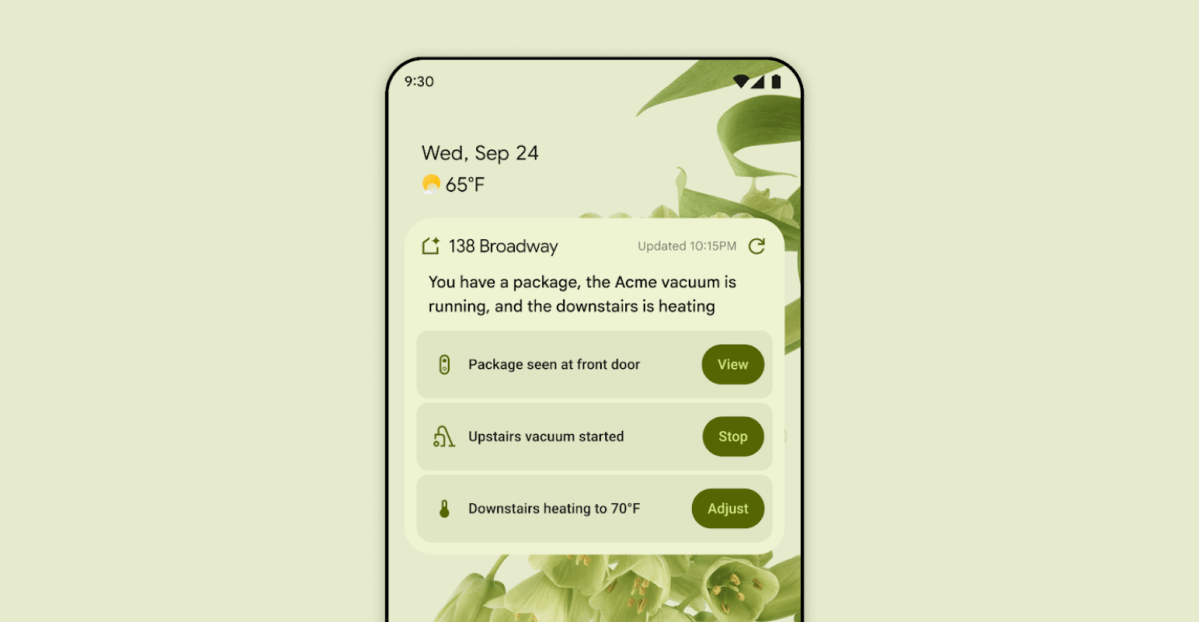
First look at the Google Home app powered by Gemini
The Verge reports Google is updating the Google Home app to bring Gemini features, including an Ask Home search bar, a redesigned UI, and Gemini-driven controls for the home.
Shadow Leak shows how ChatGPT agents can exfiltrate Gmail data via prompt injection
Security researchers demonstrated a prompt-injection attack called Shadow Leak that leveraged ChatGPT’s Deep Research to covertly extract data from a Gmail inbox. OpenAI patched the flaw; the case highlights risks of agentic AI.
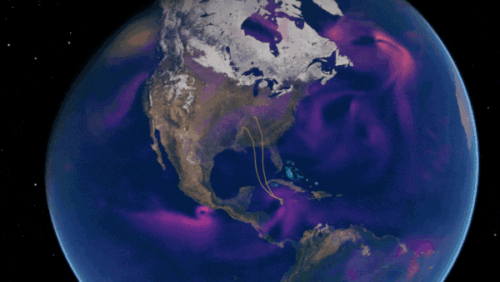
Predict Extreme Weather in Minutes Without a Supercomputer: Huge Ensembles (HENS)
NVIDIA and Berkeley Lab unveil Huge Ensembles (HENS), an open-source AI tool that forecasts low-likelihood, high-impact weather events using 27,000 years of data, with ready-to-run options.
Scaleway Joins Hugging Face Inference Providers for Serverless, Low-Latency Inference
Scaleway is now a supported Inference Provider on the Hugging Face Hub, enabling serverless inference directly on model pages with JS and Python SDKs. Access popular open-weight models and enjoy scalable, low-latency AI workflows.
Google expands Gemini in Chrome with cross-platform rollout and no membership fee
Gemini AI in Chrome gains access to tabs, history, and Google properties, rolling out to Mac and Windows in the US without a fee, and enabling task automation and Workspace integrations.
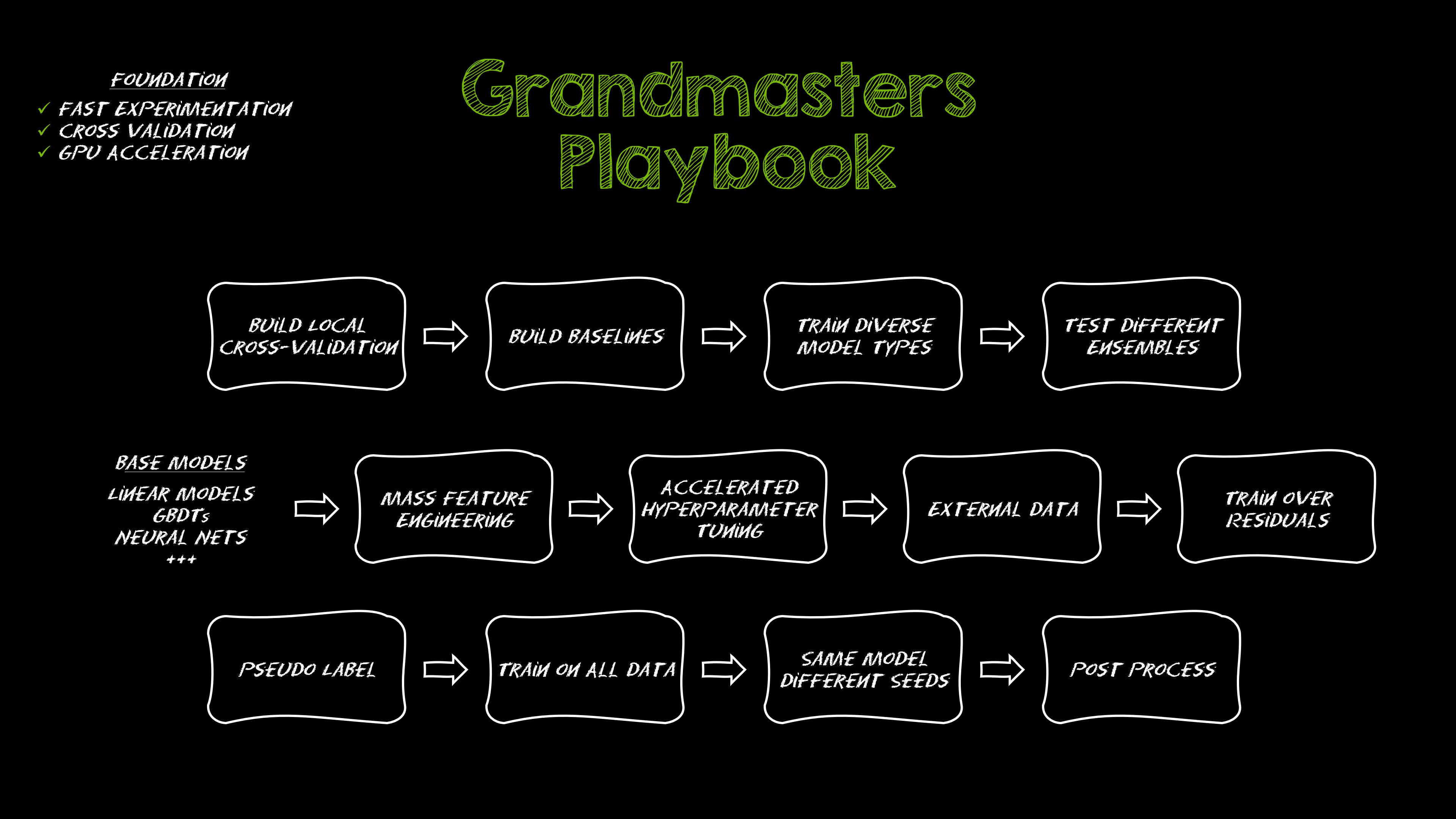
Kaggle Grandmasters Playbook: 7 Battle-Tested Techniques for Tabular Data Modeling
A detailed look at seven battle-tested techniques used by Kaggle Grandmasters to solve large tabular datasets fast with GPU acceleration, from diversified baselines to advanced ensembling and pseudo-labeling.