OpenAI launches gpt-oss-120b and gpt-oss-20b under Apache 2.0 license
Sources: https://openai.com/index/introducing-gpt-oss, openai.com
TL;DR
- OpenAI released two open-weight language models: gpt-oss-120b and gpt-oss-20b, available under the Apache 2.0 license. They are designed for strong real-world performance at a lower cost and are optimized for open deployment.
- gpt-oss-120b has 36 layers and a total of 117B parameters, with 128 total experts and 4 active experts per token. It can run efficiently on a single 80 GB GPU.
- gpt-oss-20b has 24 layers and a total of 21B parameters, with 32 total experts and 4 active experts per token. It can run on edge devices with 16 GB of memory.
- Both models demonstrate strong tool use, few-shot function calling, chain-of-thought reasoning, and performance on health and math benchmarks, while supporting OpenAI’s Responses API and on-device workflows.
- Safety remains foundational: both models underwent safety training and evaluations, including adversarial fine-tuning under a Preparedness Framework, with external review and published model cards.
Context and background
OpenAI’s gpt-oss models mark the company’s first openly-available open-weight language models since GPT-2. The two new models are designed to offer high-quality reasoning capabilities at lower cost, with an Apache 2.0 license that supports wide customization and deployment. The effort complements existing API offerings by enabling open-weight models to be hosted on user infrastructure—ranging from on-prem deployments to edge devices—while emphasizing safety evaluations and alignment with OpenAI’s Model Spec. The gpt-oss initiative comes with partnerships and real-world testing experiences with organizations like AI Sweden, Orange, and Snowflake. These collaborations explore hosting, data security considerations, and fine-tuning on specialized datasets to address practical use cases—from data protection to industry-specific tasks.
What’s new
Two models are being released: gpt-oss-120b and gpt-oss-20b. Both are built as transformers with mixture-of-experts (MoE) to reduce the number of active parameters needed to process input. Specifics include:
- gpt-oss-120b: 36 layers, 117B total parameters, 5.1B active parameters per token, 128 total experts, 4 active experts per token, context length up to 128k.
- gpt-oss-20b: 24 layers, 21B total parameters, 3.6B active parameters per token, 32 total experts, 4 active experts per token, context length up to 128k.
- Both models use alternating dense and locally banded sparse attention patterns, similar to GPT-3, and employ grouped multi-query attention with a group size of 8. They natively support context lengths up to 128k and use Rotary Positional Embedding (RoPE) for positional encoding.
- Data and training focus: a mostly English, text-only dataset with emphasis on STEM, coding, and general knowledge. Data was tokenized with a tokenizer derived from OpenAI’s o4-mini and GPT-4o families (o200k_harmony).
- Training and alignment: post-training mirrors the process used for o4-mini, including supervised fine-tuning followed by a high-compute RL stage. The objective was to align the models with the OpenAI Model Spec and teach them to apply chain-of-thought reasoning and tool use before producing answers.
- Capability and safety: the models support three levels of reasoning effort (low, medium, high) to trade latency for performance. They underwent comprehensive safety training and evaluations, including an adversarially fine-tuned variant tested under OpenAI’s Preparedness Framework, and results are documented in a research paper and model card.
- Ecosystem and accessibility: the gpt-oss models are designed to be used with OpenAI’s Responses API and integrated into agentic workflows, with strong instruction following and tool-use capabilities (e.g., web search, Python execution) and the ability to tune reasoning effort for latency-critical tasks.
Why it matters (impact for developers/enterprises)
The gpt-oss release provides a significant step toward broadly accessible open-weight LLMs with robust reasoning and tool-use capabilities. The key implications include:
- Ownership and customization: organizations can run and customize these models on their own infrastructure, enabling on-premises data handling, data security, and alignment with internal policies.
- Hardware-friendly deployment: gpt-oss-120b can run efficiently on a single 80 GB GPU, while gpt-oss-20b is designed to run on edge devices with 16 GB of memory. This lowers the barrier to on-device inference and rapid iteration without large-scale infrastructure.
- Flexibility in performance and latency: the models expose adjustable reasoning effort (low/medium/high) to balance latency and performance for diverse workflows.
- Safety and governance: OpenAI emphasizes safety as foundational, combining safety training, evaluation, and external review (via the Preparedness Framework and model cards) to maintain consistent safety standards with proprietary frontier models.
- Ecosystem and ecosystem-enabled deployments: with compatibility to the Responses API and collaboration with partners, developers can design end-to-end AI workflows that combine local inference with cloud capabilities, depending on deployment and latency needs.
Technical details or Implementation
The gpt-oss models employ a mixture-of-experts (MoE) approach to reduce the number of active parameters processed per token. Notable technical characteristics include:
- Architecture: Transformer architecture with alternating dense and locally banded sparse attention patterns, reminiscent of GPT-3, and grouped multi-query attention with a group size of 8.
- Positional encoding: Rotary Positional Embedding (RoPE) used for efficient and scalable positional representation.
- Context length: native support for context lengths up to 128k tokens.
- Tokenization: data tokenized with a superset of the o4-mini and GPT-4o tokenizer (o200k_harmony), which is being open-sourced alongside the models.
- Training and post-training: models post-trained with a process similar to o4-mini, combining supervised fine-tuning with a high-compute RL stage to align with the OpenAI Model Spec and to enhance CoT reasoning and tool use before final output.
- Active vs total experts: gpt-oss-120b uses 128 total experts with 4 active per token; gpt-oss-20b uses 32 total experts with 4 active per token.
- Performance notes: across standard benchmarks, gpt-oss-120b demonstrates competitive or superior results to several OpenAI reasoning models (e.g., o3-mini, o4-mini) on coding, math, health, and tool-use tasks; gpt-oss-20b shows similar performance to o3-mini and can outperform it in certain domains despite its smaller size.
- Safety and governance: in addition to internal safety training and evaluations, OpenAI tested an adversarially fine-tuned gpt-oss-120b version under its Preparedness Framework, with results reported in a research paper and model card. A separate emphasis is placed on ensuring open models meet comparable safety standards to frontier proprietary models.
Model specifications snapshot
| Model | Layers | Total Params | Active Params Per Token | Total Experts | Active Experts Per Token | Context Length |---|---|---|---|---|---|---| | gpt-oss-120b | 36 | 117B | 5.1B | 128 | 4 | 128k |gpt-oss-20b | 24 | 21B | 3.6B | 32 | 4 | 128k |
Key takeaways
- OpenAI provides two open-weight LLMs with strong reasoning and tool-use capabilities under the Apache 2.0 license, enabling broad customization and on-prem/on-device deployment.
- The models leverage mixture-of-experts to optimize efficiency: relatively few active parameters are used per token during inference, contributing to lower compute needs for large models.
- Both models support substantial context lengths (up to 128k) and are designed to operate across consumer hardware, including GPUs with ample VRAM and edge devices with modest memory.
- Safety is a central pillar, with comprehensive safety training, adversarial fine-tuning, and external review; detailed safety results are shared in related research and model-card documentation.
- The release is accompanied by ecosystem partnerships and documentation to support real-world deployments, from on-prem hosting to specialized fine-tuning datasets.
FAQ
-
What are gpt-oss-120b and gpt-oss-20b?
They are open-weight language models released by OpenAI, built as transformers with mixture-of-experts, designed for strong reasoning, tool use, and efficient deployment. They are available under the Apache 2.0 license.
-
Under what license are they released?
Apache 2.0.
-
How do they perform relative to other OpenAI models?
gpt-oss-120b outperforms OpenAI o3-mini and matches or exceeds OpenAI o4-mini on several benchmarks; gpt-oss-20b matches or exceeds o3-mini and can outperform it in some areas like competition mathematics and health.
-
What hardware considerations are there?
gpt-oss-120b can run on a single 80 GB GPU; gpt-oss-20b can run on edge devices with 16 GB of memory, enabling on-device use cases and rapid iteration without heavy infrastructure.
-
What safety approaches were used?
Both models underwent extensive safety training and evaluations, plus an adversarial fine-tuning variant tested under a Preparedness Framework, with findings published in a research paper and a model card.
References
More news
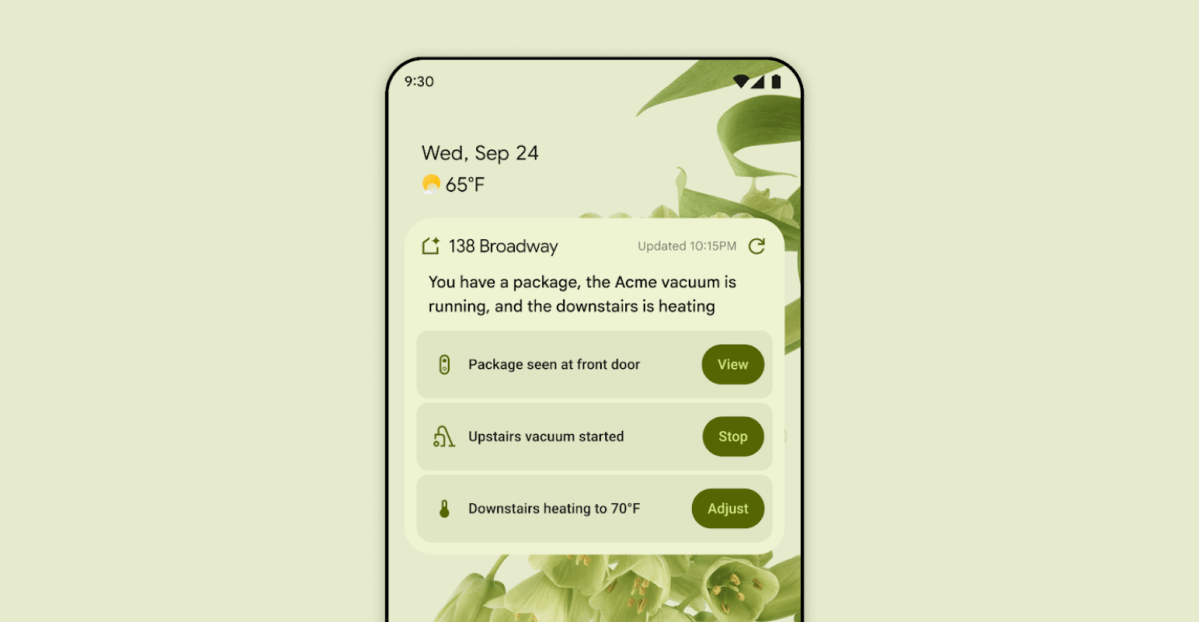
First look at the Google Home app powered by Gemini
The Verge reports Google is updating the Google Home app to bring Gemini features, including an Ask Home search bar, a redesigned UI, and Gemini-driven controls for the home.
NVIDIA HGX B200 Reduces Embodied Carbon Emissions Intensity
NVIDIA HGX B200 lowers embodied carbon intensity by 24% vs. HGX H100, while delivering higher AI performance and energy efficiency. This article reviews the PCF-backed improvements, new hardware features, and implications for developers and enterprises.
Shadow Leak shows how ChatGPT agents can exfiltrate Gmail data via prompt injection
Security researchers demonstrated a prompt-injection attack called Shadow Leak that leveraged ChatGPT’s Deep Research to covertly extract data from a Gmail inbox. OpenAI patched the flaw; the case highlights risks of agentic AI.
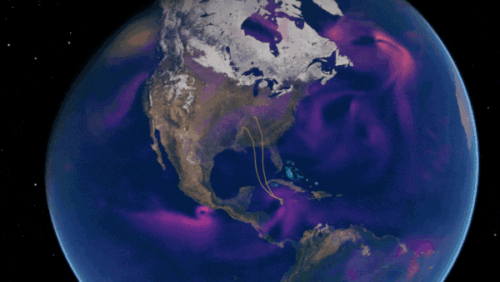
Predict Extreme Weather in Minutes Without a Supercomputer: Huge Ensembles (HENS)
NVIDIA and Berkeley Lab unveil Huge Ensembles (HENS), an open-source AI tool that forecasts low-likelihood, high-impact weather events using 27,000 years of data, with ready-to-run options.
Scaleway Joins Hugging Face Inference Providers for Serverless, Low-Latency Inference
Scaleway is now a supported Inference Provider on the Hugging Face Hub, enabling serverless inference directly on model pages with JS and Python SDKs. Access popular open-weight models and enjoy scalable, low-latency AI workflows.
Google expands Gemini in Chrome with cross-platform rollout and no membership fee
Gemini AI in Chrome gains access to tabs, history, and Google properties, rolling out to Mac and Windows in the US without a fee, and enabling task automation and Workspace integrations.